Nuclear Cardiology & Stress Tests
Diagnostic Imaging Services
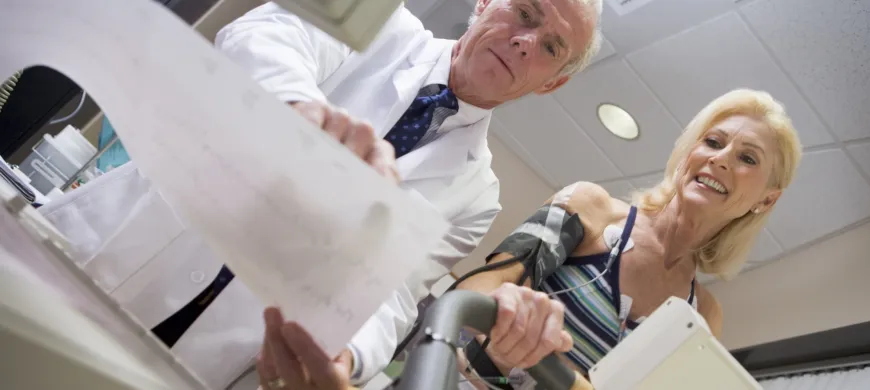
Nuclear cardiology and cardiac stress tests are used to help assess heart health and diagnose coronary artery disease and other cardiac conditions.
Cardiac Stress Testing
During a cardiac (exercise) stress test, heart activity is measured using an
electrocardiogram (EKG) as you walk on a treadmill to
assess response to stress. Small electrodes placed on various body areas track heart activity.
Treadmill speed and elevation slowly increases until
you reach a certain heart rate or need to stop.
Nuclear Cardiology Testing
During a nuclear cardiology test, a small amount of radioactive tracer is given through an IV. A nuclear medicine machine with a camera detects the tracer as it moves around your chest and takes images of your heart. Images are produced to evaluate coronary arteries, blood flow, and integrity of the heart muscle.
Exercise Stress / Treadmill EKG
An exercise stress test or treadmill EKG (Electrocardiogram) is commonly used to measure how well the heart performs during exercise or a chemically induced state, particularly in patients with symptoms of chest pain or who are at risk for coronary artery disease. Exercise stress tests may also be referred to as stress tests, exercise EKGs, or treadmill tests. During the test, you will walk on a treadmill while an EKG measures your heart activity. Every three minutes, the treadmill will slowly increase in speed and elevation. The test will end when you reach a predicted heart rate or when you need to stop.
Preparation
- Wear comfortable clothes & walking shoes
- Do not eat or drink anything except water after midnight the night before your test.
- Have no caffeine, including chocolate, for 24 hours prior to test.
- Bring a list of your current medications.
- Take blood pressure medicine as usual unless instructed otherwise by your physician.
- For diabetics only, take 1/2 insulin dose and eat a light breakfast.
Chemical Stress Test
A chemical stress test is used when a patient is unable to perform more than moderate exercise due to weakness, injury or other situations. At the onset of the test, you will be connected to an EKG machine and an IV of Lexiscan and a radiological tracer will be started in your arm. The Lexiscan is used to dilate blood vessels, simulating exercise and the radiological tracer allows for visualization of the heart and vessels via nuclear medicine imaging. (During this time, you may feel warm, experience a mild headache or tightness in your chest. These effects are normal and typically go away soon after the test.) The nuclear medicine camera will take two sets of images two hours apart: a resting set and a stressed set. Each image set takes approximately 15 minutes. The entire test lasts approximately four hours.
Preparation
- If you think you may be pregnant, please discuss with your physician prior to scheduling and please inform the technologist.
- Follow Prep for exercise stress test.
- Do not take any medications containing Aminophylline, Theophylline or dipyridamole 24 hours prior to test.
Myocardial Perfusion Scan
Also called a nuclear stress test, the myocardial perfusion scan uses a radioactive tracer to evaluate heart activity during rest and during stress. During the stress portion of the test, you will walk on a treadmill (exercise stress) or be given the medicine Lexiscan to simulate an exercise response (chemical stress). The stress portion will include EKG monitoring. Two sets of nuclear images will be taken two hours apart: one while resting and one following the stress portion. The full test takes about four hours.
Preparation
- If you are pregnant or think you may be, please inform the technologist before performing the test.
- Follow the preparation instructions for an Exercise Stress Test as specified by your physician.
- Do not take medications containing Aminophylline, Theophylline (bronchodilators) or Dipyridamole (blood thinners) 24 hours before the test. Ask your physician or pharmacist if your medicine contains these drugs.
MUGA Scan
The multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan measures how much blood is expelled with every heartbeat. You will receive two injections of radioactive tracer about 20 minutes apart. A nuclear camera takes images of your heart from different angles while the heart is being monitored by an EKG. Each image takes about 10 minutes.
Preparation
- If you are pregnant, or think you might be, please inform the technologist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will it hurt?
These tests are painless but may involve injections.
Is this test dangerous?
No. The tests are performed under the direct supervision
of a cardiologist. The radioactive tracer dose is small and
fast-acting.
When will I know the results?
Your physician will get the results in 2-3 working days
and will contact you if the results need to be discussed.
What should I wear?
Comfortable clothing.
