Ultrasound
Diagnostic Imaging Services
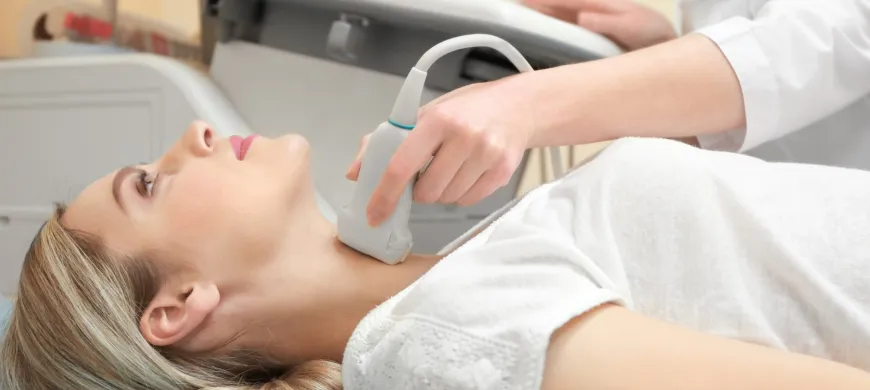
What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound imaging (sonography) uses high-frequency sound waves to view soft tissues such as muscles and internal organs. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show movement of the body's internal organs as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.
Procedure
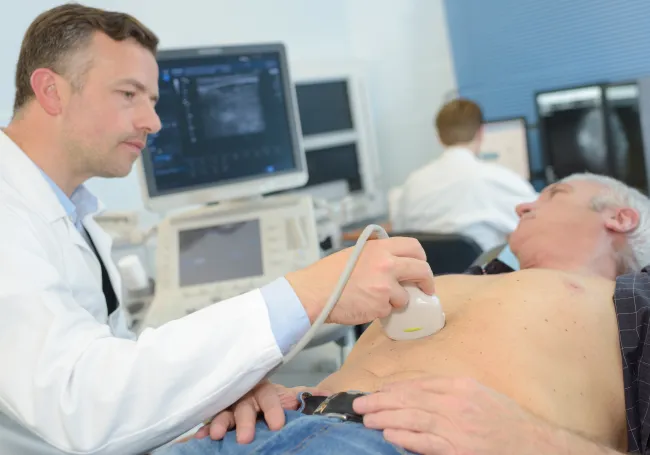
In an ultrasound exam, a hand-held transducer is placed against the skin. The transducer sends out high frequency sound waves that reflect off of body structures. The returning sound waves, or echoes, are displayed as an image on a monitor. The image is based on the frequency and strength (amplitude) of the sound signal and the time it takes to return from the patient to the transducer. Unlike with an x-ray, there is no ionizing radiation exposure with this test. During an echocardiogram, you are connected to an EKG monitor that continuously records your heart rate.
Depending on the type of exam, ultrasound procedures
typically range from 15 minutes to an hour.
Preparation
Abdomen - Complete or Limited, or Gallbaldder
- Please do not eat or drink at least 8 hours prior to exam.
- You may take your medications with a small amount of water.
Pelvic
- Please drink at least 32 ounces of fluid, beginning 2 hours before exam time (please do not urinate during this time).
Abdomen/Pelvis Ultrasound Combined
- Do not eat 8 hours prior to exam.
- Drink 32 ounces of water 2 hours before exam time.
- Do not empty your bladder prior to the test.
- Echocardiogram
- Thyroid
- Carotid Arteries
- Testicular
- Breast Unilateral/Bilateral
- Extremities
- Kidneys
